RPA (Robotic Process Automation) is a fast-growing technology. Organizations in different industries and geographical areas are starting to realize how RPA can increase their operational efficiency. In this article, we cover the benefits of RPA, it's impact on business and future evolution.
What is RPA?
RPA (Robotic Process Automation) utilizes software robots as a form of digital workforce. It has the potential to offer dramatic improvements in productivity. Software robots can deliver a high level of accuracy, speed, and consistency, while also offering strong auditability and scalability on large-scale process automations.
For what kind of tasks is RPA best suited?
- Many manual, rule-based and repetitive processes are perfect candidates for RPA, such as gathering and manipulating data from one system and inputting it into another.
- Alternative for software integrations, especially ones that involve legacy systems. RPA is often a more agile and cost-efficient option than traditional integration project, and it's relatively easy to calculate ROI for RPA projects.
Definition of RPA targets are often conducted with Lean principles and Lean diagnostics. Together with these methodologies, RPA can be used to enhance human capabilities: employees can concentrate on more creative and value-adding services instead of repetitive routines.
Benefits of RPA
Benefits of RPA include productivity boost, cost savings, improved quality of repetitive tasks and agility/scalability.
Productivity boost
- Up to 80% reduction in average handling time.
- Up to 90% reduction in average response time.
- 1 Robot = 3-5 FTEs
Cost savings
- Processing costs reduced up to 70%.
- Fast return on investment.
Improved quality
- Improvements on accuracy, reliability and audit trail.
- Staff can focus on more value-adding and complex tasks.
Agile and scalable
- From process definition to robot deployment even as fast as within 2 weeks.
- Re-use of RPA elements & fast adaptation of changed processes.
Occupational Impact of RPA
Organisations have used outsourcing and offshoring as methods to cut their costs. However, as labor costs are rising in the most popular offshoring countries, these approaches don’t necessarily provide the desired savings anymore. Although a Robotic FTE is often estimated to be equivalent of at least 3 human FTEs, RPA needs to be viewed as a tool to remove non-value adding activities rather than a tool for removing jobs.
RPA might put some traditional jobs at risk due to the efficiency provided by automation, but RPA is also generating new kinds of jobs and bringing back the previously offshored and outsourced jobs to local operators. Reshoring and restructuring of the global workforce is likely to happen.
All these factors make RPA a great candidate to enhance processes especially in accounting and finance, insurance, human resource management, help desk and support activities, but RPA can be used in many other industries as well. For example, healthcare can benefit tremendously from RPA by improving patient information handling and patient flows.
RPA Evolution and The 4th Industrial Revolution
RPA evolution is fast. Currently it's evolving from Early RPA (Phase II in the below image) to Advanced RPA (Phase III), where robots are utilizing pattern recognition learning, advanced analytics and combining elements of AI with rule-based process automation.
The next step is evolving into Smart Process Automation (SPA), where AI enables cognitive automation by utilizing multiple sources of data and natural language recognition and understanding. For example, one of our partners and leading RPA software vendors are already taking big steps in the SPA direction by teaming up with IBM and their Watson AI solution, famous for its use in the decision-making process of cancer treatment.
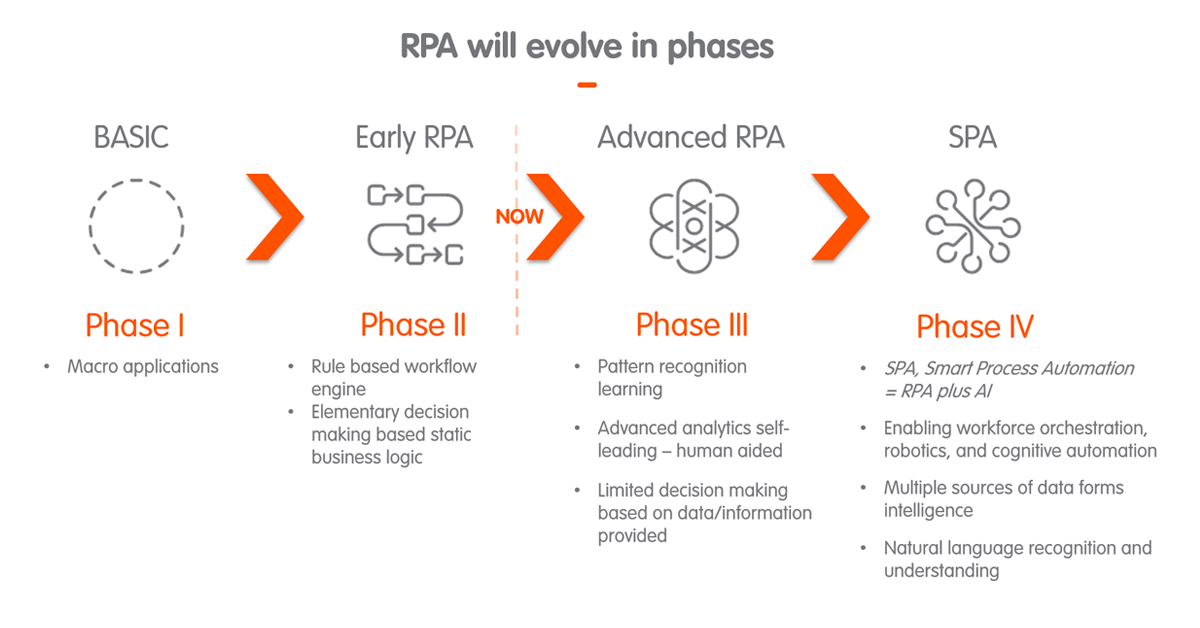
Many new RPA software vendors are entering the market with new technologies. Technical architectures of RPA solutions can be deployed as on-premise solutions or Robotics as a Service (RaaS). This allows flexibility, as organizations can choose whether to have full control of the environments including configuration and maintenance work, or to concentrate on the automation work and have the environments provided as a service.
Digitalization can be seen as the 4th industrial revolution – and RPA is a key element in this megatrend.
Written by
Toni Petäjämaa
Want to know more about RPA's opportunities? Contact us to learn more.

